3.9. Steady-State and Single-Phase Transient Hydraulics¶
3.9.1. Introduction¶
The core assembly hydraulics treatment in SAS4A/SASSYS‑1 includes the calculation of coolant flow rates and pressure distributions within each core channel. Coolant flow rates and pressures are calculated in a number of different places in the code. They are used in the steady-state thermal hydraulics initialization; the pre-voiding thermal hydraulics module calculates coolant flows and pressures; and after the onset of voiding, they are calculated in the boiling module. This section describes only the steady-state and pre-voiding calculations. Chapter 12 describes the hydraulics calculations after the onset of voiding. Chapter 14 and Chapter 16 describe the hydraulics calculations after pin disruption.
The coolant flow provides the heat removal from the fuel pins, and so the main reason for calculating coolant flow rates before the onset of voiding is to provide information for the fuel-pin temperature calculations. Core channel flow rates are also needed for the PRIMAR-4 primary loop thermal hydraulics calculations. The pressure distribution within a channel is calculated mainly to obtain the pressure-dependent coolant saturation temperature used to determine the onset of boiling.
For the steady-state initialization the user specifies the initial coolant flow rate for each channel and the outlet plenum pressure. The code then calculates the pressure distribution in each channel, starting from the outlet and working down to the inlet. The channel with the largest steady-state pressure drop is used to determine the steady-state inlet plenum pressure; and the inlet orifice coefficients in all other channels are adjusted so that all channels have the same total steady-state pressure drop.
In the transient hydraulic calculations, both the coolant flow rates and the pressure distributions are calculated for each channel. Pressure boundary conditions are used for the transient coolant flow rate calculations. The driving pressures for these calculations are the inlet and outlet coolant plenum pressures supplied by the PRIMAR-4 module. Since all channels use the same inlet and outlet pressures, flow redistribution between channels is automatically accounted for as temperatures and flows change. Extrapolated coolant temperatures are used to evaluate coolant properties in the transient hydraulics calculations, since coolant flow rates for a time step are calculated before temperatures are calculated.
Figure 3.1.2 shows the logic flow in subroutine TSCL0, the driver for pre-voiding core channel thermal hydraulics. As indicated previously, a multi-level time step approach is used for the transient calculations in SAS4A/SASSYS‑1. In general, the routines in a transient module start with all quantities knows at the beginning of a time step, and a pass through a module results in calculating the values of relevant parameters of the module for one channel at the end of the time step. Different time-step sizes can be used for different phenomena. In particular, the pre-voiding coolant hydraulics time step can be smaller than, but not larger than, the heat-transfer time step or the PRIMAR time step. One pass through TSCL0 calculates one coolant time step for one channel. If the coolant time step finishes a heat-transfer step, then the temperature calculations for the heat-transfer step are also carried out.
Figure 3.9.1 shows the logic flow in subroutine TSCNV1. This subroutine and the routines called by it carry out the pre-viding coolant flow and pressure calculations. Subroutine TSCNV1 also checks on whether to switch to the boiling model.
As indicated in Figure 3.9.2, the pre-voiding transient hydraulics module interacts with PRIMAR and TSHTRN. PRIMAR supplies the inlet and outlet pressures that drive the coolant flows in the core channels. In return, TSCL0 supplies PRIMAR with the current channel flow rates, as well as hydraulic parameters to use in estimating future flow rates for the next PRIMAR time step. TSCL0 supplies the coolant flow rates to TSHTRN, and TSHTRN computes the coolant temperatures used by TSCL0.
3.9.2. Basic Equations¶
Before the onset of voiding, the coolant is treated as incompressible, and the basic equation used for liquid coolant flow in non-voided channels is
(3.9-1)
with
\(w\) = \(w(t)\) - independent of \(z\)
\(w\) = coolant flow rate (kg/s) \(= \rho_{\text{c}} v A_{\text{c}}\)
\(A_{\text{c}}\) = coolant flow area
\(p\) = pressure
\(\rho_{\text{c}}\) = density
\(v\) = coolant velocity (m/s)
\(z\) = axial position
\(t\) = time
(3.9-2)
Figure 3.9.1 Subroutine TSCNV1, Pre-Boiling Coolant Flow Rates and Pressure Distribution¶
Figure 3.9.2 Interactions Between Pre-Voiding Transient Hydraulics and Other Modules¶
\(f\) = friction factor, approximated either as
(3.9‑3a)
\(f = \begin{cases} A_{\text{fr}}\left( \mathrm{\text{Re}} \right)^{b_{\text{fr}}} & \text{if Re} \geq \text{Re}_{\text{L}} \\ \frac{A_{\text{fL}}}{\mathrm{\text{Re}}} & \text{if Re} < \text{Re}_{\text{L}} \\ \end{cases}\)
or as
(3.9‑3b)
\(f = A_{\text{fr}}\left( \text{Re} \right)^{b_{\text{fr}}}\ + \frac{A_{\text{fL}}}{\text{Re}}\) (3.9-3a)
where \(A_{\text{fr}}\), \(b_{\text{fr}}\), and \(A_{\text{fL}}\) are user-supplied correlation coefficients
(3.9‑4)
\(\text{Re} = \frac{D_{\text{h}}w}{\mu A_{\text{c}}}\) = Reynolds number
\(Re_{\text{L}}\) = Reynolds number for the transition from turbulent to laminar flow
\(\mu\) = viscosity
\(D_{\text{h}}\) = hydraulic diameter
\(\left( \frac{\partial \text{p}}{\partial \text{z}} \right)_{\text{K}}\) = orifice pressure drop
\(g\) = acceleration of gravity
\(\rho\) = density
The axial node structure shown in Figure 3.2.3 is used for the coolant. Figure 3.9.3 shows which variables are defined at node boundaries and which are averages or integrals over the length of a node. With this mesh structure, integrating Eq. 3.9-1 over the length of the channel gives
(3.9‑5)
where
(3.9‑6)
and
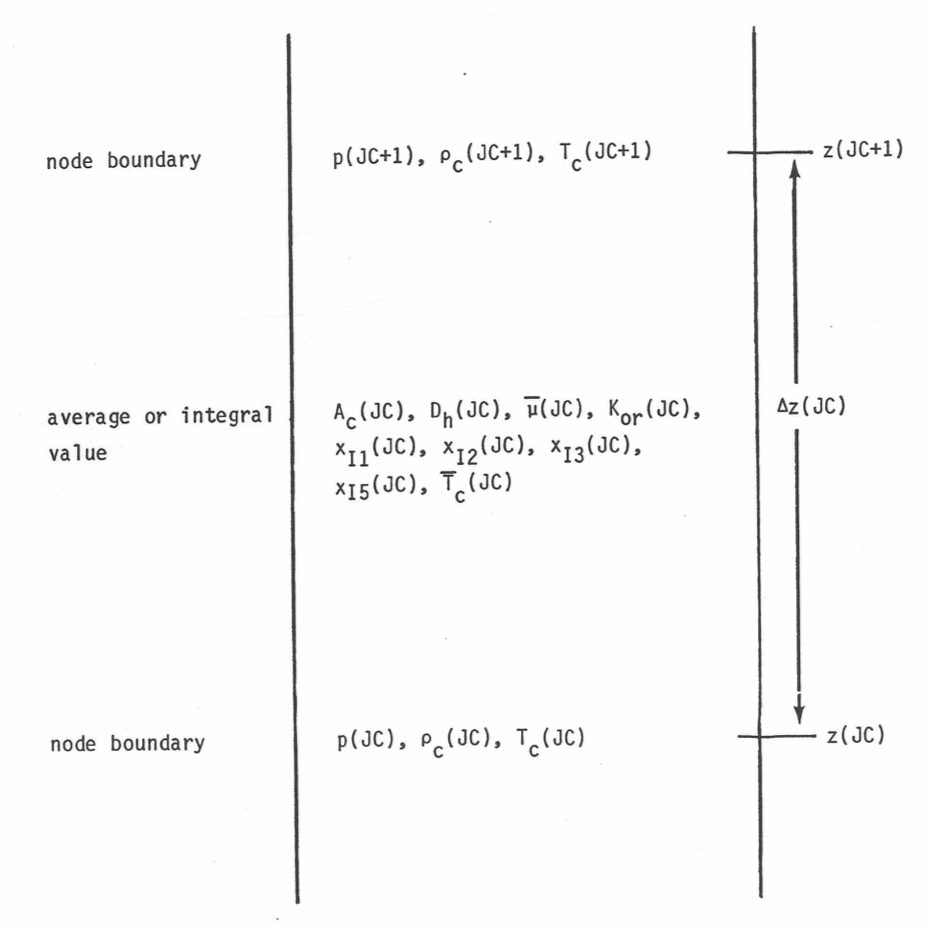
Figure 3.9.3 Interactions Between Pre-Voiding Transient Hydraulics and Other Modules¶
(3.9‑7)
\(\left( \frac{\Delta z_{\text{i}}}{A} \right)_{\text{b}}\) and \(\left( \frac{\Delta z_{\text{i}}}{A} \right)_{\text{t}}\) are effective inertial terms at the bottom and top of the subassembly.
(3.9‑8)
(3.9‑9)
(3.9‑10)
(3.9‑11)
(3.9‑12)
(3.9‑13)
(3.9‑14)
\(p_{\text{b}}\) = pressure at bottom of channel, and \(p_{\text{t}}\) = pressure at top of channel.
3.9.3. Flow Orifices¶
As mentioned in the section on the SAS4A/SASSYS‑1 channel treatment in Section 3.2, the channel is divided axially into a number of zones. One zone represents the fuel-pin region. Other zones represent regions above and below the fuel pins. At the bottom of each zone, a flow direction dependent orifice coefficient can be specified by the user. Another orifice coefficient can be used at the top of the upper zone. These orifices can represent orifice blocks, subassembly inlet and exit losses, and the pin support grid at the bottom of the pins. For each orifice, the user supplies one orifice coefficient for positive flow and another for negative flow. In addition, in the fuel-pin region, orifice coefficients representing equally spaced grid spacers can be specified. These orifice coefficients are used as the values of \(K_{\text{or}} \left( \text{JC} \right)\) in Eq. 3.9-12 for the appropriate axial nodes. The effect of each orifice is spread evenly over an axial node, rather than concentrated at a point.
3.9.4. Finite Difference Equations - Coolant Flow Rates¶
If \(w_{1} = w\left( t \right),\ w_{2} = w\left( t + \Delta t \right),\ \Delta w = w_{2} - w_{1}\), then we approximate \(\Delta w\) as
(3.9‑15)
and
(3.9‑16)
in which \(\theta_2\) is the degree of implicitness. For small time steps a semi-implicit calculation is used, with \(\theta_1\) = \(\theta_2 = .5~\). For a fully implicit calculation for large time steps, \(\theta_1 = 0\) and \(\theta_2 = 1.0~\). The value used for \(\theta_2\) is
(3.9‑17)
where
(3.9‑18)
and \(\tau\) is the time constant for flow rate changes given by
(3.9‑19)
The definition of \(d_1\) is given by Eq. 3.9-25 below. This correlation for \(\theta_2\) is discussed in Section 3.19.1. The additional approximations are made that
(3.9‑20)
(3.9‑21)
(3.9‑22)
These equations are combined to give
(3.9‑23)
where \(p_{\text{t}1}\) and \(p_{\text{t}2}\) are the pressures at the top of the subassembly at the beginning and end of the time step. Similarly, \(p_{\text{b}1}\) and \(p_{\text{b}2}\) are the pressures at the bottom of the subassembly at the beginning and end of the time step, respectively.
Solving for the coolant flow rate change, \(\Delta w\), gives
(3.9‑24)
where
(3.9‑25)
The temperatures used to evaluate \(\rho_{\text{c}}\) and \(\overline{\mu}\) in Eqs. 3.9-9, 3.9-11, and 3.9-14 are extrapolated coolant temperatures, extrapolated to the end of the coolant step.
3.9.5. Coolant Pressures¶
After the flow rate has been calculated, the coolant pressures in a channel at the end of a time step are calculated. First, the pressure at node \(\text{MZC}\), the last node at the top of the subassembly, is calculated as
(3.9‑26)
where
(3.9‑27)
\(z_{\text{plu}}\) = outlet plenum elevation
\(\rho_{\text{cout}}\) = density at outlet
\(p_{\text{x}2}\) = coolant outlet plenum pressure at the end of the time step
Note that \(p_{\text{x}2}\), the outlet plenum pressure supplied by the primary loop module, is defined at an elevation \(z_{\text{plu}}\), the elevation of the upper plenum, whereas \(p\left( \text{MZC} \right)\) is calculated at \(z\left( \text{MZC} \right)\), so the gravity head term occurs in Eq. 3.9-27.
After \(p\left( \text{MZC} \right)\) has been calculated, the other pressures are calculated, starting at node \(\text{MZC}\)-1 working down, using
(3.9‑28)
In Eqs. 3.9-25 and 3.9-28, the value used for \(\frac{\partial w}{\partial t}\) is calculated at the end of the time step for the transient calculation as
(3.9‑29)
The pressure, \(p_{\text{b}2}\) at the bottom of the subassembly at the end of the time step is calculated as
(3.9‑30)
\(z_{\text{pll}}\) = plenum location. Note that \(p_{\text{in}2}\), the inlet plenum pressure supplied by he primary loop module, is defined at an elevation \(z_{\text{pll}}\), the elevation of the lower plenum.
The pressure distribution in the steady state is calculated the same as in the transient, except that \(\frac{\partial w}{\partial t}\) is zero in the steady-state calculation.