2.8.1. Appendix 2.1: SAS4A/SASSYS‑1 Standard Input Description
SAS input data is read from a simple text file that is provided on the command line. The input file is normally provided via input redirection:
$ sas.x < model.inp > model.out
where model.inp is the model input file, model.out is the
intended output file, and the executable, sas.x, depends on the
version and platform being used.
Starting with Version 5.3, command-line arguments may also be used. The input and output files may be specified as the first and second positional arguments:
$ sas.x model.inp model.out
or they may be specified using command-line options:
$ sas.x --input model.inp --output model.out
Short versions of the command-line options (-i and -o
respectively) may also be used.
An additional command line option is available to override the default port to which SAS binds when listening for incoming connections to coupling interfaces. The default port is 60439, but this can be changed with the following:
$ sas.x --port <port>
This type of interface is used, for example, with the
coupled RVACS model. Instead of defining the
port on the command line, SAS will also recognize the environment
variable __SAS_ENV_BIND_PORT__. If both the environment variable
and the command-line option are used, the command-line option takes
priority.
2.8.1.1. Input Format
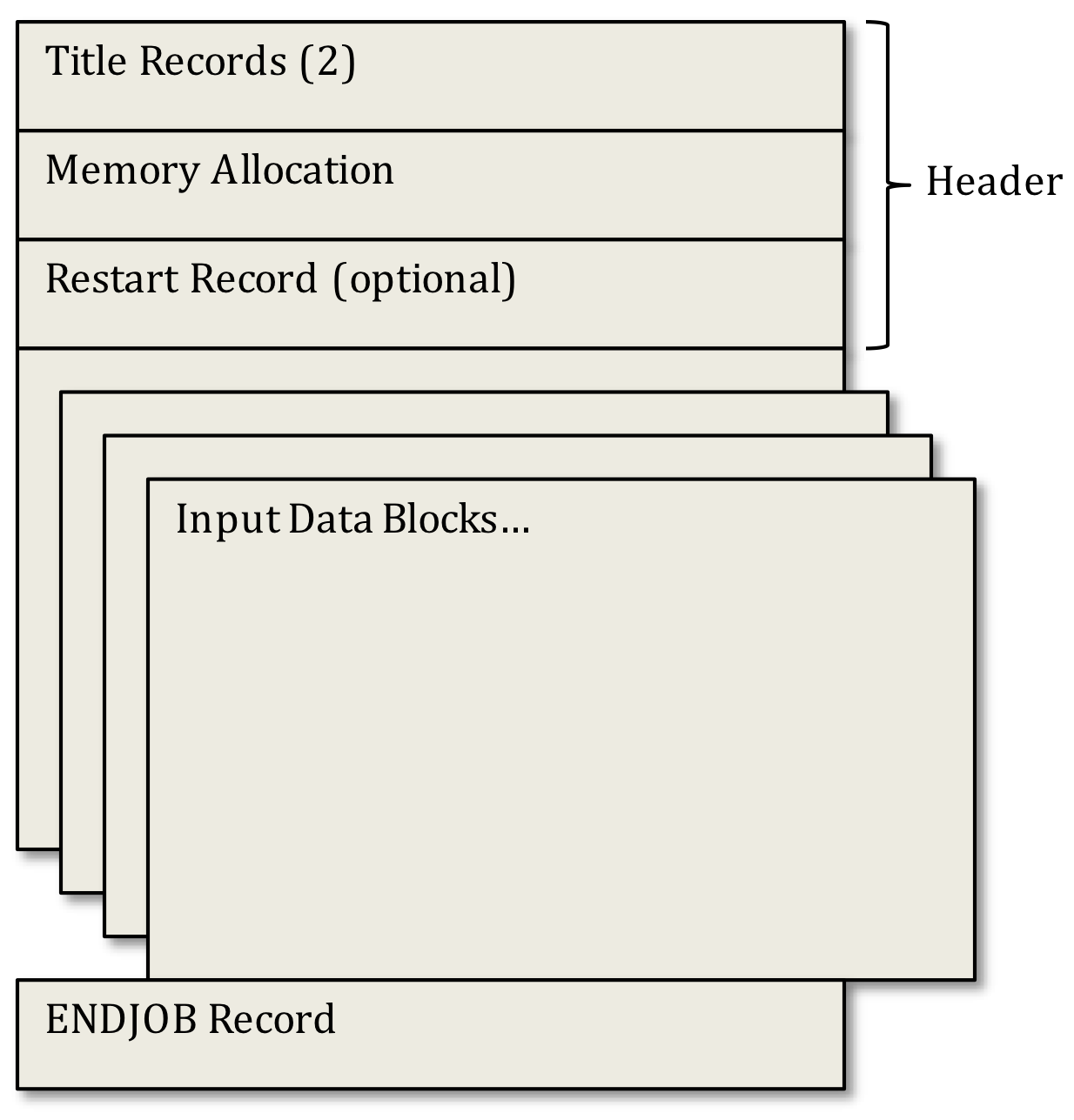
A SAS model file has the following structure:
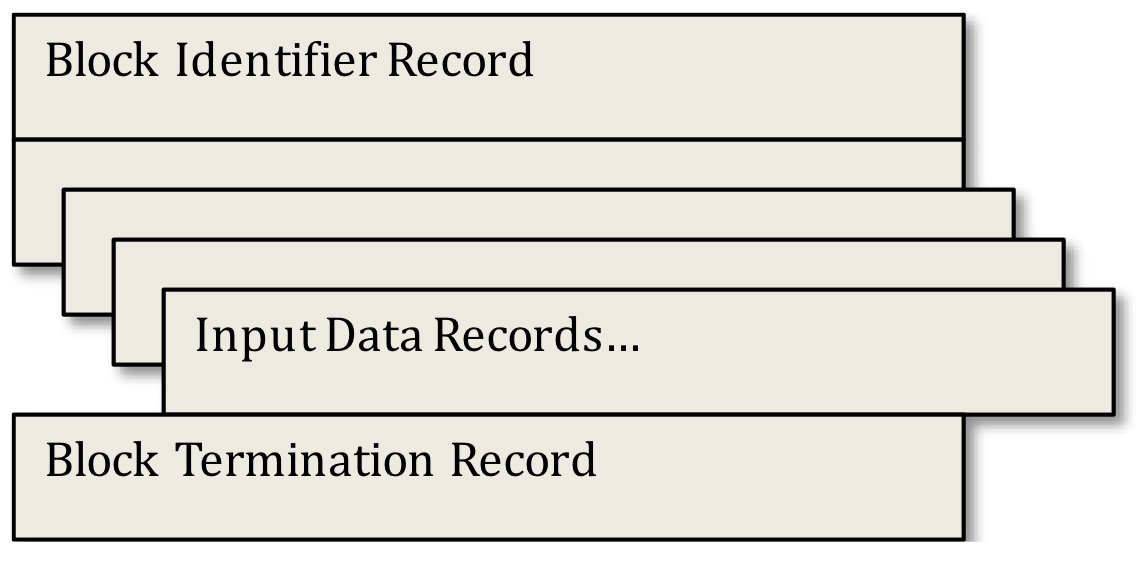
where the Input Data Blocks have the following structure:
With the exception of the title records, any text following a comment
character (! or #) will be stripped from the input before being
parsed. When searching for the first title record, if any non-blank text
exists before a comment character, then the comment is considered to be
part of the title. The second title record must immediately follow the
first.
2.8.1.2. Input Data Records Descriptions
Each input file for SAS4A/SASSYS‑1 begins with a file header that includes two title records (primary and secondary) along with memory allocation information and an optional restart record. The first 72 characters of the primary and secondary title records will appear as a heading at the top of each page break in the printed output. Both title records are required.
Primary Title Record
form = "(A72,A8)"
read(*,form) TITLE(1), VERNAM
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
TITLE(1) |
Primary Title (72 characters) |
VERNAM |
The major and minor code version label for this input deck. For Version X.y.z, the version label is the eight character string X.ybbbbb
left adjusted in columns 73 through 80, where “b” is a blank character (space). The version label must match the current code version in order for execution to proceed beyond the reading of the primary title record. |
Secondary Title Record
form = "(A72)"
read(*,form) TITLE(2)
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
TITLE(2) |
Secondary Title (72 characters) |
Storage Allocation Record
form = "(I6,9I3)"
read(*,form) NCH, NEUTSP, IDBUGP, IPDECK, NBYSSH, &
IDATMO, IADEFC, IAPLUC, IACNTL, IALBOP
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
NCH |
Number of channels for this case (see NCHAN). Maximum value is 22000. |
NEUTSP |
Neutronics storage allocation flag. Set > 0 when spatial kinetics modules are used. Only relevant with distributions that include coupled spatial kinetics capabilities. |
IDBUGP |
Data management print flag. Set > 0 when data storage allocation and data movement diagnostic prints are desired. |
IPDECK |
Input data editing flag. Set > 0 to generate a compiled copy (i.e. redefinitions eliminated, last defined values retained) of the input deck output as an ASCII file “INPUT.dat”. |
NBYSSH |
Number of bypass channels involved in subassembly-to-subassembly heat transfer. |
IDATMO |
No longer used. |
IADEFC |
Data pack DEFC storage allocation flag. Set > 0 to eliminate storage allocation for data pack DEFC (DEFC is necessary for DEFORM-4 and DEFORM-5). |
IAPLUC |
Data pack PLUC storage allocation flag. Set > 0 to eliminate storage allocation for data pack PLUC (PLUC is necessary for PINACLE, LEVITATE, and/or PLUTO-2). |
IACNTL |
Control system module data storage allocation flag. Set > 0 to eliminate storage allocation for control system module data and input data block INCONT. |
IALBOP |
Balance-of-plant module data storage allocation flag. Set > 0 to eliminate storage allocation for balance-of plant module data and input data blocks IINBOP and FINBOP. When the balance of plant model is activated, steam generators do not participate in the null transient. |
Neutronics Storage Allocation Record
The neutronics storage allocation record should be present only
when NEUTSP > 0.
form = "(2I12)"
read(*,form) MAXFCM, MAXECM
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
MAXFCM |
Number of single precision words in data buffer array. |
MAXECM |
Number of single precision words in data storage array. |
RESTART Directive
The RESTART directive is required only for cases that initiate with the reading of a restart file from binary data file “RESTART.bin”.
form = "(A8, I4, I6)"
read(*,form) NAMBLK, NUMBLK, IRN
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
NAMBLK |
“RESTART” (left justified) |
NUMBLK |
100 |
IRN |
Restart number on the restart file that this case will use. If IRN =
999, the restart used will be the last restart written on the restart
file. If IRN = 0, the first restart written on the restart file will be
used. (IRN > 0 is used only for the multiple restart option. See
|
INCLUDE Directive
Note
New in Version 5.3.
Syntax:
INCLUDE <file>
An INCLUDE directive instructs the SAS input processor to read additional data from an external file. Once SAS has completed reading the external file, input processing continues with the next line in the current file. Included files may, themselves, have INCLUDE directives, however recursively including a file that is currently being read will result in an error.
INCLUDE directives are only interpreted in the body of the input file. The directive may not appear before a RESTART directive or before the memory allocation record.
Included files may not contain title records, memory allocation records, or RESTART or ENDJOB directives. They may contain any other input fragment that, when taken into context with the surrounding input, produces a valid SAS model file.
SAS records a log of all input read in the SAS.log file. The log file has been updated to report both the file and line number for each line of input.
Comment Records
Syntax:
# comment 1
! comment 2
! etc...
A comment record is any input record whose first non-blank character
is a ! or # symbol. Arbitrary text may follow the comment character.
Comment records have an advantage over XNOTES input blocks
in that they may occur anywhere within an input description, including
between the input records of other input blocks.
Block Identifier Record
The block identifier record is required as the first record of each input block.
form = "(A8, I4, 2I6)"
read(*,form) NAMBLK, NUMBLK, ICH, IZERO
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
NAMBLK |
Block name (left justified). |
NUMBLK |
Block number (see Table I). |
ICH |
Channel number (use 1 if NUMBLK < 51). |
IZERO |
0, Zero block background input before reading data. Do not use 0 for data input following the reading of a restart file. >0, Channel number of that block of the same name whose input data is to be used as background input before reading data. Background input blocks must be previously defined. Use IZERO = ICH for data input during a restart. |
Block Input Data Records
Within each block, input data is read in a format consistent with the data type for that block: integer, floating point, or character. See the list of Formatted Input Blocks below for the data type associated with each input data block.
NUMBLK |
NAMBLK |
Input Format |
|---|---|---|
1 |
INPCOM |
Integer |
3 |
INPMR4 |
Integer |
5 |
INCONT |
Special Mixed |
6 |
IINBOP |
Special Integer |
7 |
INEUTR |
Integer |
11 |
OPCIN |
Real |
12 |
POWINA |
Real |
13 |
PMATCM |
Real |
14 |
PRIMIN |
Real |
15 |
FINBOP |
Special Real |
16 |
RNEUTR |
Real |
17 |
ANEUTR |
Character |
18 |
PMR4IN |
Real |
51 |
INPCHN |
Integer |
61 |
GEOMIN |
Real |
62 |
POWINC |
Real |
63 |
PMATCH |
Real |
64 |
COOLIN |
Real |
65 |
FUELIN |
Real |
Fixed Format Integer Input
form = "(2I6,10I6)"
read(*,form) LOC, NUM, IDATA(LOC:LOC+NUM-1)
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
LOC |
Initial block location for data input. |
NUM |
Number of input data to be read into the IDATA fields ( |
IDATA |
Input data definitions to be placed in locations (LOC) to (LOC+NUM-1) in the input block. |
Fixed Format Floating Point Input
form = "(2I6,5F12.0)"
read(*,form) LOC, NUM, RDATA(LOC:LOC+NUM-1)
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
LOC |
Initial block location for data input. |
NUM |
Number of input data to be read into the RDATA fields ( |
RDATA |
Input data definitions to be placed in locations (LOC) to (LOC+NUM-1) in the input block. |
Fixed Format Character Input
form = "(2I6,10A6)"
read(*,form) LOC, NUM, CDATA(LOC:LOC+NUM-1)
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
LOC |
Initial block location for data input. |
NUM |
Number of input data to be read into the CDATA fields ( |
CDATA |
Input data definitions to be placed in locations (LOC) to (LOC+NUM-1) in the input block. |
Free-Formatted Input (New in Version 5.3)
Syntax:
<LOC> : <DATA> [<DATA>...]
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
LOC |
Starting block location for data input. |
DATA |
Input data definitions to be placed in the input block beginning at location (LOC) and continuing until all input is consumed on the line. |
Free formatted input may be used for integer or floating point data
blocks. Free-format lines require the specification of the initial
location, LOC followed by a colon (:) and any number of space-,
comma-, or tab-delimited input values in sequential location order. The
initial location value may be indented with leading white space.
Optional whitespace may be on either side of the colon, which is
required. At least one numeric value must be present after the colon.
Consecutive spaces and tabs are treated as a single white space. However consecutive commas are significant and cause the corresponding input location to be skipped. Comments may follow the data.
Input blocks may contain both fixed- and free-formatted records, however the data type must be compatible with the block type. Listing 2.8.1 provides an example of free-formatted input.
#---+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7----+----8
#
# INPCOM: Channel Independent Variables (Integer)
#
INPCOM 1 0 0
#
# MAXSTP: Maximum Number of Main (Power and Reactivity)
# | Time Steps
11 : 0 !MAXSTP
#
# IPO: Number of Steps between Prints before IBLPRT or Boiling
# | IPOBOI: Number of Steps between Prints after IBLPRT
# | | or Start of Boiling
# | |
12 : 1000 1000 #IPO, IPOBOI
#
# NOREAC: Main Time Step Intevals between PSHORT print
# |
41:1000
#
# ICLCMP: Flag to Save Plot Data for Transients to Unit 11
# |
24: 1 !ICLCMP
-1
#---+----1----+----2----+----3----+----4----+----5----+----6----+----7----+----8
Block Termination Record
Syntax:
END
The block termination record is required as the final record of each input block.
As an alternative to the END statement, SAS still recognizes a fixed-formatted input record where LOC = -1 as a block termination record.
ENDJOB Directive
The ENDJOB directive indicates the final line of input. Input processing
terminates when this record is encountered.
form = "(A8, I4)"
read(*,form) NAMBLK, NUMBLK
Input |
Description |
|---|---|
NAMBLK |
“ENDJOB” (left justified) |
NUMBLK |
-1 |
XNOTES Block
Format:
form = (A72)
read(*,form) COMMENT
Comments can be added in the input file as a pseudo input block
called XNOTES. The block begins with a block identifier record
having the block name ‘XNOTES’, followed by any number of comment lines.
The block ends with an END statement or a ‑1 in columns 5-6. The
comment records are not stored and are not transferred to the edited
input data file INPUT.dat or the restart file RESTART.dat.
Example:
XNOTES 1 (block identifier)
.
.
.
(COMMENTS)
.
.
.
END (block delimiter)
FUNCTION Block
Function input blocks allow users to construct arbitrary functions that can be referenced by other input and models. Five types of user functions can be defined: table lookup (interpolated), field, user-defined (parsed), external dynamic library, and control system.
General syntax:
FUNCTION <id> "<name>"
TYPE = <type>
[...]
END
Function blocks are identified by the keyword FUNCTION followed by a unique id and name. Function blocks are terminated by an END statement. The type parameter is required, while the presence of other parameters depends on the type. Five values correspond to the five types of user functions that are presently supported: TABLE, FIELD, USER, EXTERNAL, and CONTROL.
The remaining parameters that can be used are source, func, arg, and kind. Interpretation of these parameters depends on the type of the function being defined. In addition, function blocks may contain table blocks, but these are only relevant for table lookup functions.
As examples, functional inputs may be used to specify transient
external reactivity or power (see NPREAT), coolant inlet temperature
for PRIMAR-1 (see NT0TAB), coolant driving pressure or normalized
coolant flow rate for PRIMAR-1 (see NPRES), or ALMR EM Pump trip time (see ILRPMP).
Additional uses for function blocks are described throughout the manual.
Internally, arguments are passed to function blocks as elements of a one-dimensional array, and each function returns a scalar result. The number of arguments passed to the function block depends on the model invoking the function. Therefore the interface is implicit, and it is up to the user to provide a meaningful function block. The function block defines how, or even if, the arguments are used.
As an example, a function block can be used to represent power or
reactivity, similar to how the PREATB and PREATM
input works, and it will be passed the current simulation time. The
function block is expected to use the argument to determine the current
power or reactivity. A TABLE function block will use the argument to
interpolate over a table of values. However, if a CONTROL function block
is used in this case, it will ignore the argument and simply return the
current value of the specified control signal.
Table Lookup Functions:
Table lookup functions can be used to define a variety of interpolations based on a user-supplied data table. For example, linear interpolation of the first four squares can be accomplished with the following function block:
FUNCTION 4 Squares
TYPE = TABLE
TABLE 2 Data
x y
0 0
1 1
2 4
3 9
4 16
END
END
Table lookup functions support four parameters: source, func, arg, and kind. The four parameters are all optional. Interpretation of these parameters is shown in Table 2.8.2.
Parameter |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
source |
Table id of local data source to be used for interpolation |
First table found in function |
arg |
Column label of independent variable in the data source table |
First column |
func |
Column label of dependent variable in the data source table |
Second column |
kind |
Type of interpolation to be performed |
Linear |
Using these parameters, users can provide more complex data tables and have more control over the type of interpolation that will be performed. Extending the previous example, the following function will perform natural spline interpolation of the first four squares:
FUNCTION 4 Squares
TYPE = TABLE
SOURCE = 2
ARG = x
FUNC = y2
KIND = Spline
TABLE 2 Data
row x y1 y2
1 0 0 0
2 1 1 1
3 2 2 4
4 3 3 9
5 4 4 16
END
END
The available types of interpolation are summarized in Table 2.8.3. In all cases, interpolating values that occur before the first (or after the last) argument in the data table will use the first (or last) function value. No extrapolation is performed. Source data tables may be of arbitrary length, limited only by available memory.
Interpolation KIND |
Description |
|---|---|
Linear |
Linear interpolation of successive values in the source data table. |
LogLinear |
Linear interpolation of the natural logarithm of successive values in the source data table. The returned value is the exponential of the interpolated value. |
Spline |
Natural (cubic) spline fit that enforces continuity in the value and first and second derivatives at each data point. For closure, a natural spline defines the second derivative to be zero for the first and last data points. |
LogSpline |
Natural spline fit that enforces continuity in the logarithm of the value and first and second derivatives at each data point. |
HermiteL0 |
Quadratic fit based on second-order Hermite polynomials that enforces continuity of the value and first derivative at each data point. The slope at each interior point is determined by a weighted average of the slopes of the two adjacent intervals. For closure, the slopes at the end points are set to zero. |
HermiteL1 |
Same as HermiteL0, except that the slopes at the first and last points are taken as the slopes of the first and last intervals, respectively. |
HermiteQ0 |
Quadratic fit based on second-order Hermite polynomials that enforces continuity of the value and first derivative at each data point. The slope at each interior point is determined by a parabolic fit with the two adjacent data points. For closure, the slopes at the end points are set to zero. |
HermiteQ1 |
Same as HermiteQ0, except that the slopes at the first and last points are taken as the slopes of the first and last intervals, respectively. |
HermiteQ2 |
Same as HermiteQ0, except that the slopes at the first and last points are taken as the slope of the adjacent interpolating parabola. |
Field Functions:
Field functions can be used to perform two-dimensional interpolation over a tabulated field of data. For example, bilinear interpolation of the sum of two values can be accomplished with the following function block:
FUNCTION 8 Sum
TYPE = FIELD
TABLE 1 FieldData
x/y 0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 2 3 4
1 1 2 3 4 5
2 2 3 4 5 6
3 3 4 5 6 7
4 4 5 6 7 8
END
END
Field functions support two parameters: source, and kind. Both parameters are optional. If source is not provided, the first table contained in the function will be used. Currently only bilinear interpolation is supported for field functions. If kind is not specified, it will default to the only option, BiLinear.
Field functions use the entire source table as the data field. The first column in the data table is interpreted as the coordinate values for the first dimension. The second and subsequent column labels in the TABLE block are interpreted as coordinate values for the second dimension. The first label is required but ignored.
Given the following source table:
where fi,j=f(xi,yj) is the function value at the coordinate xi, yj, bilinear interpolation can be performed for any x, y coordinate pair. If
then
where
If either coordinate falls outside the range of the provided coordinates, flat, constant extrapolation is performed. More specifically:
User-Defined Functions:
User-defined functions support a basic syntax for building complex expressions from mathematical operators and functions. For example, a sinusoidal function can be defined with the following function block:
FUNCTION 3 Sinus
TYPE = USER
ARG = t
FUNC = "pi := 3.14159; 2.0*sin(pi*t)"
END
The two parameters arg and func are required for user functions. Values for source and kind are ignored.
Parsing and evaluation of user-defined functions is handled by the open-source fparser library [2-10]. As shown in the example above, the function syntax supports inline variables and numeric literals. Logical expressions are also supported. For example,
FUNCTION 2 Squares
TYPE = USER
ARG = x
FUNC = "if(x>0,x^2,0)"
END
will return the square of positive values of x, and zero otherwise. For details on the supported syntax, see Reference [2-11].
External Dynamic Functions:
Compiled functions contained in external dynamic libraries (dylib on macOS, DLL on Windows, and shared objects on Linux) can be accessed via an external function. For example, given a dynamic library MyLib.dylib that contains the function MyFunc, the function block would be defined as follows:
FUNCTION 7 ExternLib
TYPE = EXTERNAL
SOURCE = MyLib.dylib
FUNC = MyFunc
END
With this definition, SAS4A/SASSYS‑1 will dynamically load “MyLib.dylib” and link to the function “MyFunc”. The source and func parameters are required. Other parameters are ignored.
Control System Functions:
The Control System module can react to and interact with many plant state variables. To support interaction with the plant state outside the Control System, a control function block can be defined. This function block requires that a control system model be defined by an INCONT block elsewhere in the input. A control function has the following simple form:
FUNCTION <id> <name>
TYPE = CONTROL
FUNC = <signal> # e.g. FUNC = 23
END
The single parameter func defines which signal number to access in the Control System model. This signal number may come from a demand table or may be the output from a block signal in the control system logic. Arguments to this type of function block are ignored.
EMPUMP Block
Model data for Equivalent Circuit EM pumps is specified using EMPUMP blocks. The syntax of EMPUMP blocks is discussed here, while the specific input data requirements for each EM pump model is discussed in Chapter 5.
General syntax:
EMPUMP <#> <type> ["<name>"]
<param1> = <param1_value> ! comment
[...]
[<paramN> = <paramN_value>] # comment
[function_block1]
[...]
[function_blockN]
[table_block1]
[...]
[table_blockN]
END
Each EMPUMP block is denoted by the block identifier line, itself containing the case-sensitive EMPUMP specifier, a unique integer block number, the model type (SIMPLE or DETAILED, case-sensitive), and an optional block name. The block internals include required and optional keyword/value entries, in addition to optional FUNCTION and TABLE block entries, followed by the keyword END to terminate the block.
Rules of the EMPUMP block are as follows:
Keyword entries are case-insensitive and may be defined in any order
Separate keyword/value entries may be separated by a newline character, a comma, or whitespace within a line
Whitespace between the keyword, value, and “=” sign is ignored
FUNCTION and TABLE blocks may be defined within the EMPUMP block, in which case they have local scope, or outside the EMPUMP block as standalone blocks, in which case they have global scope
Blocks defined within the EMPUMP block may come before or after any of the keyword/value entries
Multiple parameters may call to the same within-scope FUNCTION block
All required keyword/value entries for a given pump must be specified within a single EMPUMP block
Parameters provided multiple times within a block take the value specified closest to the end of the block
Comments may be placed in EMPUMP blocks using either the “!” or “#” characters, after which any characters on the line are ignored
At the moment, the model type may be either “SIMPLE” or “DETAILED”, corresponding to the simple and detailed equivalent circuit models, respectively.